 |
||
 |
||
This page covers the following topics:
In general, it is recommended that you use a popular and well supported Linux distribution like Ubuntu Linux or Red Hat Linux (either x86 or amd64). If you plan to install CrashFix on Ubuntu, it is recommended to use an LTS (long term support) release of Ubuntu Server, for example Ubuntu Server 12.04 LTS or Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS. Non-LTS releases are not recommended to use, because of their short support period.
In order to install and use CrashFix debug info uploader tool, you need the following system requirements to be satisfied:
From a command shell, run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install apache2
sudo apt-get install php5
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-php5 php5-gd
The commands above download from repository and install the latest available versions of Apache HTTP Server, PHP engine and PHP extension modules for Apache.
Your web files will now be located in /var/www directory.
CentOS or Red Hat Linux
From a command shell, run the following commands:
sudo yum install httpd
sudo yum install php php-gd php-dom
The commands above download from repository and install the latest available versions of Apache HTTP Server, PHP engine and PHP extension module for Apache.
Next, run the following commands to add Apache HTTP Server to autorun and start it:
sudo chkconfig --level 235 httpd on
sudo service httpd start
Your web files will now be located in /var/www/html directory.
In order to install MySQL database, type the following:
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
sudo apt-get install mysql-client
sudo apt-get install php5-mysql
The commands above install MySQL server component, MySQL client component and MySQL extension module for PHP, respectively.
CentOS or Red Hat Linux
In order to install MySQL database, type the following:
sudo yum install mysql-server
sudo yum install mysql
sudo yum install php-mysql
The commands above install MySQL server component, MySQL client component and MySQL extension module for PHP, respectively.
Run the following commands to add MySQL server to autostart and start the server:
sudo chkconfig --level 235 mysqld on
sudo service mysqld start
During the installation of the MySQL database server, a root user is created. You need to create a MySQL root user password. You will need the password for creating other MySQL server users.
To connect to the MySQL server enter the following command:
mysql -u root -p
The MySQL command prompt appears. At the command prompt enter the following command and press Enter (in the command below, replace the <your_password> placeholder with some password):
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('<your_password>');
If the command is executed successfully, the following message is displayed:
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Now we need to create a new database schema that will store CrashFix tables. To do this, type the following:
CREATE SCHEMA crashfix;
The command above creates empty schema that we will populate later.
Next, we want to create another database user named crashfix that will be used by CrashFix web application for connecting to database. To create the user, type the following (in the command below, replace the <your_password> placeholder with some password):
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON crashfix.* TO 'crashfix'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '<your_password>';
The command above creates the user named 'crashfix' and grants the user all privileges on 'crashfix' database schema.
Finally, type 'quit' to exit the MySQL prompt.
To check that Apache and PHP are installed and running, create phpinfo.php file in Apache document root directory.
Note: Typically, the Apache document root directory is /var/www (in Debian or Linux Ubuntu) or /var/www/html (in CentOS or Red Hat Linux).
In the phpinfo.php file, enter the PHP method phpinfo() as follows:
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Open the file in your browser. The standard PHP information page should display.
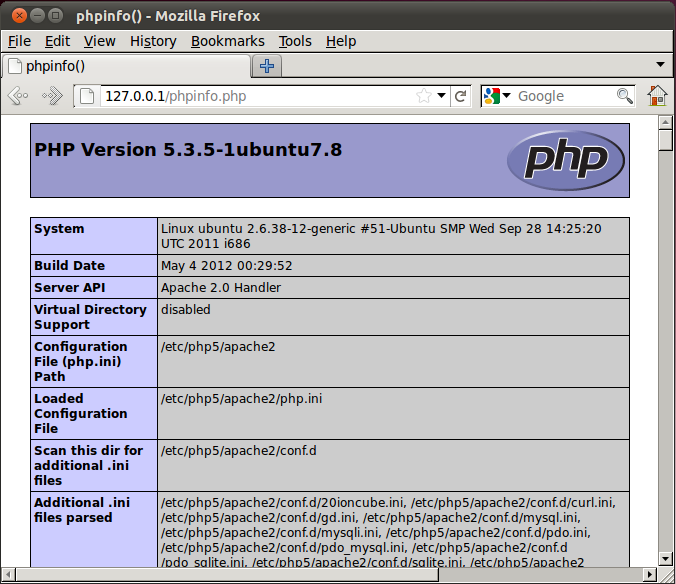
PHP information page
At this point, you should have Apache HTTP server + PHP + database (MySQL or SQLite) installed.
Download CrashFix web application archive from our Download page.
Unpack the archive:
tar xzvf crashfix-webapp-1.0.x.tar.gz
Next, move the files to web server's document root directory:
Note: Typically, the document root is /var/www directory (in Debian or Linux Ubuntu) or /var/www/html directory (in CentOS or Red Hat). Below, we denote the document root directory as DOCUMENT_ROOT%, and you should replace this placeholder with the actual directory path.
sudo mv crashfix DOCUMENT_ROOT
If everything is OK, you should have CrashFix files in DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix directory:
DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix
index.php | CrashFix web application entry script
assets/ | The directory where temporary resources (like images and CSS files) will be published
protected/ | This directory content is protected from direct access by .htaccess file
...
config/ | This directory contains configuration files
data/ | This directory will contain crash reports and debug info files
...
runtime/ | This directory will contain logs and temporary files
Edit the DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix/protected/config/user_params.ini config file and specify the correct database connection string, login and password. For additional information on config file fields and their meaning, please refer to comment lines that can be found in the config file.
Note: To edit the config file, you can use Midnight Commander editor or another editor. For example, the commands below install Midnight Commander (in Linux Ubuntu) and open the config file in it. When ready, press F10 to quit the editor.
sudo apt-get install mc
sudo mcedit DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix/protected/config/user_params.ini
From a command shell, run the following command:
sudo chmod -R 0755 DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix
The command above makes DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix directory, its subdirectories and files readable and writable for Apache webserver.
The following command sets Apache webserver user to be the owner of DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix directory and its subdirectories (typically, Apache webserver runs as 'www-data' user of 'www-data' group in Debian or Linux Ubuntu or as 'apache' user of 'apache' group in CentOS or Red Hat Linux). If your system is Debian or Linux Ubuntu, type the following command:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix
If your system is CentOS or Red Hat Linux, type the following:
sudo chown -R apache:apache DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix
Now, you can try to open the CrashFix web application in your web browser. To do this, type 'http://localhost/crashfix/index.php' in your browser's navigation bar and press Enter. Typically, you should see the following in your browser (see the image below):

Webapp login page
sudo php DOCUMENT_ROOT/crashfix/protected/yiic.php migrate
When prompted, press 'y' and then press 'Enter'. If everything is OK, the following message appears:
Migrated up successfully.
Congratulations! Your CrashFix web application is now installed!
First of all, download an appropriate CrashFix package (RPM or DEB) from our Download page. If your server is running Debian or Linux Ubuntu, you should download DEB package. If your server is running CentOS or Red Hat, you should download RPM package.
When the package has been downloaded, install it by typing the following (for DEB package):
sudo dpkg -i <package_name>
or (for RPM package):
sudo yum install <package_name>
In both the cases above, you should replace the <package_name> placeholder with the file name you have downloaded.
If everything is OK, you should have the following directories and files:
/usr/sbin/crashfixd | The CrashFix daemon executable file /etc/crashfix/crashfixd.conf | The CrashFix daemon configuration file /etc/init.d/crashfixd.sh | The CrashFix shell script /var/log/crashfix/ | The directory where CrashFix daemon places its log files /var/run/crashfix/ | The directory where CrashFix daemon places its PID-file
Edit the config file /etc/crashfix/crashfixd.conf. For additional information on config file fields and their meaning, please refer to comment lines in the config file.
Now we want to add CrashFix service to autostart (this will automatically start CrashFix service on system boot).
If your system is Debian or Linux Ubuntu, type:
sudo update-rc.d -f crashfixd defaults
If your system is CentOS or Red Hat Linux, type:
sudo chkconfig --level 235 crashfixd on
Next, start the CrashFix service by typing the following command:
sudo service crashfixd start
The expected output of the last command is the following:
Checking if crashfixd process exists... Could not read PID file /var/run/crashfixd.pid: No such file or directory Forked the CrashFix daemon process: pid = <pid>.
To ensure CrashFix service is running, type the following command:
ps aux | grep crashfixd
The command above prints the list of processes having 'crashfix' in process name. The expected output is the following (in the output below, some unimportant characters were omitted and replaced by the ... placeholder):
root <pid> ... /usr/sbin/crashfixd --start -c /etc/crashfix/crashfixd.conf root <pid> ... /usr/sbin/crashfixd --start -c /etc/crashfix/crashfixd.conf
There should be two processes launched under the root user: the daemon process and the monitoring process. The monitoring process is a process whose purpose is to check daemon's status periodically and restart the daemon on critical errors.
Download the CrashFix uploader tool ZIP archive from our Download page. Then unpack the archive to a directory of your choice.
You should have the following executable files in the directory:
To get help on available uploader commands, type the following:
uploader.exe --help
Note: By default, PHP doesn't allow to upload large files (larger than 2MB). In order to upload large symbol files, you may need to edit your php.ini configuration file and modify the post_max_size and upload_max_filesize parameters. Setting these with 100MB would typically be sufficient (if you plan to upload very large PDB files up to 1 GB in size, than better set these with 1024MB). Do not forget to restart your Apache webserver after editing the config file.
 1.5.9
1.5.9